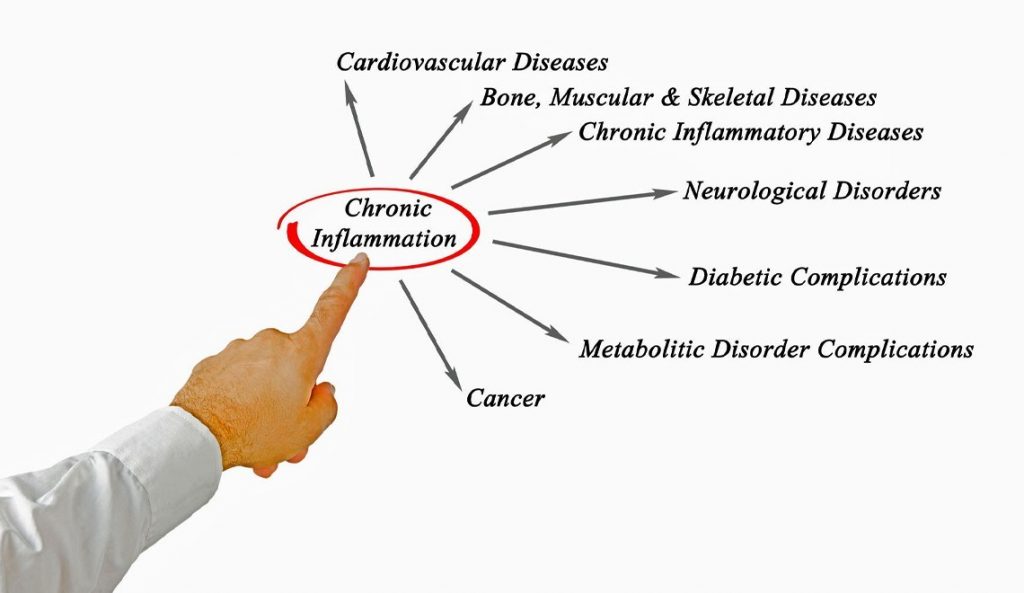
Chronic inflammation is due to immune system imbalance. If we can redress that, we can help reduce the risk of health problems. —like skin disorders, joint pains, digestive issues, migraines, anxiety, and mood swings—that many people experience as a result. Recent research suggests that chronic symptoms are associated with many modern diseases, including obesity and heart disease. Also, it can make you feel tired and fatigued.
As a qualified and practicing remedial therapist for the past 30 years, I have treated and cared for an extraordinary number of clients who suffer from chronic pain. Acute is the initial response of the body to harmful stimuli. It is the increased movement of plasma and leukocytes (especially granulocytes) from the blood into the injured tissues.
Inflammation is right in the short term. It’s part of our immune system’s natural response to heal an injury or fight an infection. However, it should stop after the damage and or the disease gone. Yet, if it becomes a long-lasting pattern, enduring, or “chronic,” symptoms are seen in many diseases and conditions.
Inflammation is responsible for many life-altering conditions and diseases—starting with heart disease to obesity, diabetes, and many autoimmune disorders.
Some researchers of heart disease believe that when fats in the wall of coronary arteries, the body produces inflammatory chemicals since it sees this as an “injury” to the core.
It is directly linked to type 2 diabetes. Experts say obesity causes inflammation, which makes it difficult for the body to use insulin.
That may be one reason why losing weight and keeping it down is crucial to reducing your chance of getting type 2 diabetes.
“arthritis” is seen as osteoarthritis, in which the tissue that supports joints, cartilage, breaks down, particularly as people age.
Rheumatoid arthritis is different. The immune system attacks joints, causing some damage to your bones. Symptoms of pain, stiffness, and red, warm, swollen joints will occur.
Our immune system drives the inflammatory process in disease. Unfortunately, Western medicine offers no definite answers as to managing or overcoming this process. The traditional approach is generally to contain the immune response with immunosuppressive agents, such as steroids. This approach is doesn’t stop the underlying disease or allows for damaged tissues to regenerate and heal.
Unless you turn off the actual cause, all that will happen is potentially more tissue damage will occur by allowing the condition to continue.
Gut Dysfunction and Inflammatory Diseases
Inflammatory diseases begin with an autoimmune reaction. To be effective at managing or to overcome a virus, there needs to be a focus on all levels.
As the gut becomes unable to process and make use of the nutrients and enzymes that are vital to proper digestion, the digestion in time is impaired, and absorption of nutrients is affected. As more inflammation occurs, your body initiates an attack. It responds to allergic reactions and other symptoms.
It begins to make sense for the reason that the pain and dysfunction, along with the body’s capacity to be inflamed, is necessary for normal cell repair processes to occur.
It is when the regulation of the cause untreated or controlled that we begin to have a problem. It has found that many of the inflammatory diseases we suffer from are gut intervened but not presenting as gut issues.
Therefore the question of what we eat is crucial is the discuss
Your Diet Does Matter
The food you eat may have a direct effect on how much inflammation you have. Eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, plant-based proteins (like beans and nuts), fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, and using healthier oils, like olive oil.
Include probiotics, like yogurt, and limit processed foods and eliminate polyunsaturated food from your diet.
Exercise and Sleep
If you have a condition like RA, activity is essential. It helps you maintain a healthy weight, which is another way to keep your health in check.
Research indicates that when healthy people are sleep-deprived, they are more susceptible to inflammation. It is unclear how, but it can be related to metabolism.
Smoking Makes It Worse
It may be hard to stop — but keep trying! Ask your doctor for their advice.
Spices Hold Promise
Ginger root has anti-inflammation perks. Cinnamon, clove, black pepper, and turmeric (which give curry powder its orange-yellow color) are also beneficial.
You are taking NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) to reduce inflammation and ease the pain. Some of these need a prescription. Others, like ibuprofen and naproxen, are available over the counter. They work if you take them regularly, tell your doctor, because they can cause stomach problems, like ulcers or bleeding. Blood clots more likely to happen, which could lead to a heart attack or stroke.
Ten signs most common in chronic inflammation
Overweight
Fat cells produce inflammatory chemicals—and extra belly fat determines how many chemicals they create.
Your blood glucose levels are high.
High blood sugar increases the number of inflammatory cytokines circulating in your blood. Increased levels of molecules called advanced glycation end products (AGEs), create inflammation.
Do you have digestive problems like gas, diarrhea, bloating, or constipation?
These come about from an overly leaky gut—and a leaky gut that allows toxins to escape into your blood is one of the leading causes of chronic inflammation throughout your body.
You’re tired all the time.
Inflamed cells are infected cells, and they can’t produce the energy you need to feel refreshed and invigorated. You may feel fatigued even when you first get out of bed—and by afternoon, you’re exhausted.
You have eczema or psoriasis, or your skin is red and blotchy.
It could be an external sign of internal fire. (There is an essential link between psoriasis and inflammatory conditions that manifest internally, including diabetes and cardiovascular disease.)
You have allergies.
If you’ have watery eyes and a runny nose, you could be chronically inflamed.
Your face is puffy.
It is a common sign of internal swelling.
Do you have gum disease?
It is another outward clue.
You suffer from “brain fog.”
It can affect your brain chemistry, causing changes in how you think and feel.
Erectile dysfunction.
Chronic inflammation will present signs that may be a cause of this problem.
How to heal this chronic condition:
These signs can point to chronic inflammation, here’s the good news: You can start taking control by changing your lifestyle.
Begin by cutting out highly inflammatory foods like sugar and grains out of your diet and eating more lean protein, vegetables, and healthy fats. Exercise daily, get enough sleep and de-stress yourself with mindfulness meditation. It is a problem you can start solving right now with a simple prescription: a smarter, healthier lifestyle.
FOOD Does MATTER.
Studies have shown that 1 in 12 women and 1 in 24 men are dealing with full-blown autoimmune-mediated swelling. People with chronic inflammation will often claim no dietary involvement. It is an inaccurate assumption, because the autoimmunity may be affected by factors not strictly related to diet, and the food can become a secondary trigger later in the development of the condition.
Lifestyle: (Stress, Over-exercising, Poor Sleep, Blood Sugar Dysregulation, Poor Social Behaviors.) Lifestyle factors are huge
Lifestyle: Create conditions of love & appreciation, keep positive attitudes, maintain proper exercise (training to peak fitness exercises), have an adequate sleep, restore blood sugar balance, and facilitate healthy social interactions.
Dietary Support: Control blood sugar levels, and promote intestinal integrity with proper flora and nitric oxide and glutathione pathways. Include fermented foods and supplements as may be needed.
An extensive range of health problems, like chronic pain, obesity, ADD/ADHD, peripheral neuropathy, diabetes, heart disease, stroke, migraines, and cancer.
It can harm your gut
Many immune cells cluster around the intestines, says Denning. Those immune cells disregard healthy bacteria that live in the stomach, creating a chronic condition.
It can harm your joints
When inflammation develops in the joints, it may cause severe damage. The condition is rheumatoid arthritis (RA)—another example of an autoimmune disorder that appears to have a genetic component, is linked to smoking, a lack of vitamin D, and other risk factors.
It’s linked to heart disease
Any injury can trigger the inflammatory process, even the insides of blood vessels. The formation of plaque in the arteries can become chronic.
Can be linked to a higher risk of cancer
Chronic inflammation is related to diseases of the lung, esophagus, cervix, and digestive tract, among others. A 2014 Harvard University study concluded that obese teenagers with high levels of inflammation had 63% of increased risk of developing colon cancer during adulthood.
It may sabotage your sleep
Case Western Reserve University 2009 study indicated that people who reported sleeping more or less than average rest had elevated levels of inflammation-related proteins in their blood than those who said they slept about 7.6 hours a night. This research found a correlation between the two (and not a cause-and-effect), so the study authors say they can’t be sure whether it triggers long and short sleep duration or whether it happens during sleep. It’s possible that a different underlying issue, like chronic stress or disease, causes both. Shift work increases the symptoms in the body.
It’s terrible for your lungs
When chronic inflammation occurs in the lungs, fluid accumulation and narrowing of the airways develop, making breathing difficult. Infections, such as asthma, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis, are all characterized by the inflammatory processes in the lungs.
Smoking, or exposure to air pollution or household chemicals, being overweight, and even consumption of cured meats cause the lungs to be inflamed.
It makes weight loss more difficult
Obesity is another major cause, and losing weight is one of the most effective ways to fight it. Elevated levels of proteins can also make weight loss more difficult than it should be. For starters, this chronic condition can influence hunger signals and slow down metabolism, so you eat more and burn fewer calories
It damages bones
Inflammation may interfere with bone growth and even promote increased bone loss, according to a 2009 review published in the Journal of Endocrinology. Concerning rheumatoid arthritis, can also have implications because it limits people’s physical activity and can keep them from performing weight-bearing, bone-strengthening exercises.
How to Evaluate Inflammatory Diseases
Since the gut commonly mediates inflammation, it is a logical starting point in the evaluation process of any patient.
There are seven common areas of causative factors for gastrointestinal dysfunction that create the environment for chronic inflammation.
Here are the key triggers within the category of evaluation:
Diet: Alcohol, Gluten, Processed Foods, Sugar, Fast Food
Medications: Corticosteroids, Antibiotics, Antacids,
Infections: Such as Yeast or Bacterial, Viral or Parasite Infection
Stress:
Hormonal: Thyroid, Progesterone, Estradiol, Testosterone
Neurological: Brain Trauma, Stroke,
Metabolic: inflammatory end products of sugar metabolism, Intestinal Inflammation, Autoimmune
