Introduction
Joint pain is a common complaint among individuals of all ages, affecting everything from daily activities to quality of life. It can range from mild discomfort to severe pain, and it often involves inflammation or injury to the joints, which are essential for movement and flexibility. It may affect a single joint, such as the knee or shoulder, or multiple joints, which can indicate systemic conditions like arthritis. In this article, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatments for joint pain to help you manage and prevent discomfort effectively.
Causes of Joint Pain
Joint pain can arise from various causes, ranging from acute injuries to chronic health conditions. Some of the most common causes include:
Arthritis:
One of the most frequent causes is arthritis, which encompasses different types, including osteoarthritis (wear and tear of cartilage) and rheumatoid arthritis (an autoimmune condition). Both types lead to inflammation and pain in the joints.
Injury:
Accidents or injuries, such as sprains, strains, and fractures, can damage the bones, cartilage, ligaments, or tendons in the joints, leading to pain and swelling.
Bursitis:
Bursae are tiny fluid-filled sacs that cushion joints. When they become inflamed, bursitis can cause pain and restricted movement.
Tendinitis:
Tendinitis is inflammation or irritation of a tendon, often resulting from repetitive movements. It commonly affects joints like the elbows, knees, or shoulders, leading to localized pain and stiffness.
Gout:
Gout is a form of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. It often affects the big toe but can also cause severe pain in other joints.
Infection:
Infections can sometimes reach the joints, causing septic arthritis, which is characterized by intense pain, swelling, and fever. This condition requires immediate medical attention.
Autoimmune Diseases:
Conditions such as lupus or psoriatic arthritis can cause inflammation in multiple joints, leading to chronic pain and stiffness.
Symptoms of Joint Pain
The symptoms can vary depending on the underlying cause, but common symptoms include:
- Pain or Discomfort: This can range from a dull ache to sharp, throbbing pain.
- Stiffness: Joint stiffness, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity, is a hallmark of arthritis.
- Swelling: Inflammation around the joint can cause noticeable swelling and tenderness.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Joint pain often limits your ability to move the affected joint fully.
- Warmth and Redness: In some cases, joints may feel warm to the touch and appear red, particularly in cases of infection or inflammatory arthritis.
- Weakness: Persistent joint pain can lead to weakness in the surrounding muscles, making movement more difficult.
Urgent Medical Attention for Severe Joint Pain
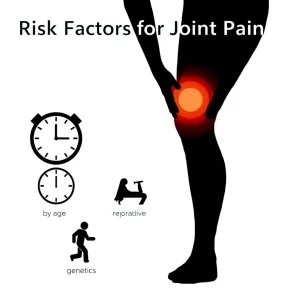
Risk Factors for Joint Pain
Several factors increase the likelihood of development, including:
- Age: As the joints wear down, the risk of developing joint pain, mainly due to osteoarthritis, increases with age.
- Previous Injuries: Joint injuries from the past, such as sprains or fractures, increase the risk of developing joint pain in the future.
- Obesity: Excess weight places additional stress on weight-bearing joints like the knees and hips, increasing the risk of pain and injury.
- Occupations or Hobbies: Jobs or activities that require repetitive movements or involve heavy physical labor can put a strain on the joints, leading to pain.
- Genetics: A family history of joint conditions, such as arthritis, can increase the likelihood of experiencing joint pain.
Effective Treatments for Joint Pain
Treatment depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. Below are several effective treatment options:
- Over-the-Counter Medications Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen and naproxen can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Acetaminophen is another option for pain relief, but it does not reduce inflammation.
- Physical therapy plays a significant role in restoring joint function, especially after injury or surgery. A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise plan to strengthen the muscles around the joint, improve flexibility, and alleviate pain. This customized approach can give you hope for a successful recovery, knowing that there are effective strategies to restore your joint health.Exercise and Weight Management Regular, low-impact exercise like swimming, walking, or cycling can help maintain joint flexibility and strengthen the muscles that support the joints. For those carrying excess weight, weight loss can significantly reduce pressure on the joints, particularly the knees and hips.
- Heat and Cold Therapy Applying heat can relax muscles and increase circulation, which helps alleviate stiffness and joint pain. Cold therapy is helpful in reducing inflammation and numbing sharp pain, especially after an acute injury.
- Corticosteroid Injections In more severe cases, corticosteroid injections directly into the affected joint can provide long-lasting pain relief and reduce inflammation. These injections are often used for conditions like arthritis or bursitis.
- Assistive Devices For those with chronic joint pain, using assistive devices like braces, splints, or canes can provide support and reduce strain on the affected joint, making movement more accessible and less painful.
- Joint Supplements Some people find relief from joint pain by taking supplements such as glucosamine and chondroitin, which may help maintain cartilage health. However, the effectiveness of these supplements can vary, and it’s essential to consult a doctor before using them.
- Surgery In cases where joint pain is caused by significant damage, such as severe arthritis or a torn ligament, surgery may be necessary. Standard surgical procedures include joint replacement, arthroscopy (a minimally invasive procedure), or joint fusion.
Preventing Joint Pain
Prevention is possible by adopting certain lifestyle habits and taking care of your joints. Here are some tips for preventing joint pain:
- Stay Active: Regular exercise keeps the joints flexible and strengthens the surrounding muscles, reducing the risk of injury and strain.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Managing your weight reduces pressure on weight-bearing joints like the knees and hips.
- Practice Good Posture: Maintaining proper posture when standing, sitting, and lifting can reduce stress on the joints.
- Protect Your Joints: If you participate in activities that put stress on your joints, consider using protective gear, such as knee pads or braces, to prevent injury.
- Warm-Up and Stretch: Always warm up before exercise and stretch afterward to maintain joint flexibility and prevent injury.
Conclusion
Joint pain is a common condition that can range from mild discomfort to debilitating pain, affecting your ability to perform daily tasks. Understanding the causes and symptoms of joint pain is the first step in finding effective treatment. Whether your joint pain is due to arthritis, an injury, or another condition, there are several treatment options available, from medication and physical therapy to lifestyle changes and surgery. By staying active, maintaining a healthy weight, and taking preventive measures, you can keep your joints healthy and reduce the risk of pain.